Today, we will get the height of fluid on capillary action by surface tension. Usually we know the maximum height formula but not generalized formula. So we will derive the generalized formular by Newtonian mechanics and Lagrangian mechanics.
Capillary action will be like the picture(FBD) below.
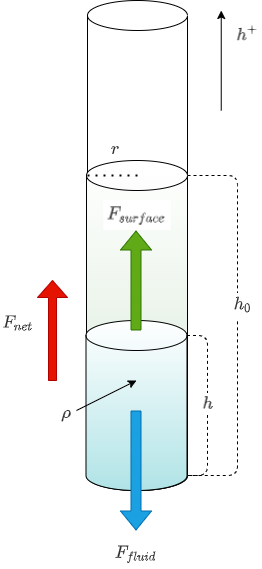
Newtonian Mechanics
By Newton’s second law, the equation of motion is \(F_{net}=F_{surface}-F_{fluid}\)
Surface tension is defined as
\[F_{surface}=\sigma \cdot l\\ \therefore \ F_{surface}=\sigma\cdot(2\pi r)\cdot cos\theta=\rho \pi r^2gh_0\]Gravity force of fluid is
\[F_{fluid}=mg=\rho \pi r^2gh\]To get net force, first we need to get linear momentum(p) and differentiate it by time(t)
\[p=mv=\rho \pi r^2 h\dot{h}\\F_{net}=\frac{dp}{dt}=\frac{\partial{p}}{\partial{h}}\frac{dh}{dt}+\frac{\partial{p}}{\partial{\dot{h}}}\frac{d\dot{h}}{dt}\\\therefore F_{net}=\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2+\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}\]Therefore, the equation of motion is
\[EoM:\ F_{net}+F_{fluid}=F_{surface}\\\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2+\rho \pi r^2gh=\sigma(2\pi r)cos\theta\\\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2+\rho \pi r^2gh=\rho \pi r^2gh_0\\\therefore \ h\ddot{h}+\dot{h}^2+gh=gh_0\]Lagrangian Mechanics
Lagrangian and Lagrangian equation is
\[L=T-V\\ \frac{d}{dt}\frac{\partial{L}}{\partial{\dot{h}}}-\frac{\partial{L}}{\partial{h}}=F_{external}\]Derive kinetic energy and potential energy,
\[V =\int{mg\ dx}= \int_h{\rho \pi r^2gh\ dh}=\frac12\rho \pi r^2gh^2\\ T=\int{F_{net}\ dx}=\int_h{F_{net}\ dh}\\=\int_h{\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2+\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}\ dh}\\=\frac12\rho\pi r^2h^2\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2h\dot{h}^2\]So, the Lagrangian is
\[L=\frac12\rho\pi r^2h^2\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2h\dot{h}^2-\frac12\rho \pi r^2gh^2\]solving the Lagrangian equation,
\[\frac{\partial{L}}{\partial{\dot{h}}}=2\rho\pi r^2h\dot{h}\\\frac{d}{dt}\frac{\partial{L}}{\partial{\dot{h}}}=2\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+2\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2\\\frac{\partial{L}}{\partial{h}}=\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2-\rho\pi r^2gh\\F_{external}=F_{surface}=\sigma\cdot(2\pi r)\cdot cos\theta=\rho \pi r^2gh_0\] \[\therefore \ 2\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+2\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2-(\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2-\rho\pi r^2gh)=\rho \pi r^2gh_0\\\rightarrow\rho\pi r^2h\ddot{h}+\rho\pi r^2\dot{h}^2+\rho \pi r^2gh=\rho \pi r^2gh_0\\\therefore \ h\ddot{h}+\dot{h}^2+gh=gh_0\]